gennaio 23, 2024
1475
The 2N4401 transistor stands as a fundamental component in the realm of electronic circuits, renowned for its NPN configuration and versatile applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the operational intricacies of the 2N4401, encompassing its pinout, specifications, equivalent transistors, and practical circuits. Understanding the key parameters, such as gain value (hfe), current limitations, and operational regions, is essential for harnessing the full potential of the 2N4401 in diverse electronic applications.
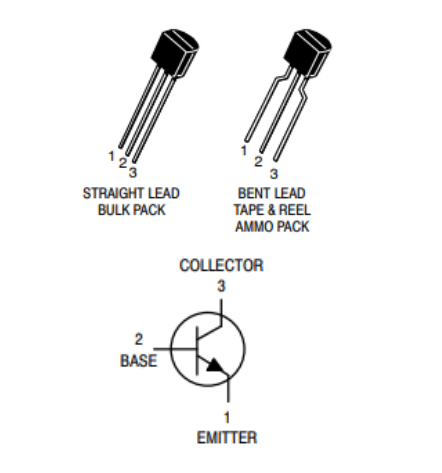
The 2N4401 transistor, manufactured by Multicomp Pro, is a through-hole component designed for general-purpose switching applications. It belongs to the NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) transistor type and features a silicon planar epitaxial structure. Enclosed in a TO-92 metal can package, this transistor offers ease of integration into various electronic circuits.
Key specifications of the 2N4401 include a collector-emitter voltage (Vce) rating of 40V, making it suitable for applications where moderate voltage handling is required. The continuous collector current (Ic) is specified at 600mA, indicating its capability to handle currents up to this level in a sustained manner. The power dissipation of the transistor is documented at 625mW, providing insights into its ability to dissipate heat generated during operation.
The hFE of the 2N4401 transistor is specified as 500. This value represents the DC current gain, indicating the amplification capacity of the transistor. In practical terms, when a small current flows into the base (IB), the transistor allows a larger current to pass from the collector to the emitter, and the hFE value of 500 quantifies this amplification factor.
When selecting an equivalent transistor, it's crucial to consider specific circuit requirements, such as voltage, current, and frequency, to ensure proper functionality. Transistor datasheets should be consulted for detailed specifications.
2N3904: Another NPN transistor widely used for general-purpose amplification. It shares similarities with the 2N4401, such as its NPN configuration.
2N2222: NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly employed for switching and general-purpose amplification. It has similar characteristics to the 2N4401 and is frequently used in electronic circuits.
BC547: A general-purpose NPN transistor known for its low noise and high gain. It is suitable for various applications, including signal amplification.
P2N2222A: Similar to the 2N2222, it is an NPN transistor utilized for switching and amplification purposes. The "P" in the prefix indicates it is a plastic-encapsulated version.
ECG123AP: An equivalent replacement for the 2N4401, ECG123AP is designed to offer similar performance in electronic circuits.
BC537, BC538, BC549: These are NPN transistors with varying characteristics, often chosen based on specific circuit requirements. They are part of the BC5xx series commonly used in audio amplifiers.
BC636, BC639: NPN transistors suitable for high-current applications. They are often utilized in power amplifier circuits.
2N2369: NPN transistor used for low-power applications and switching. It can be used as a substitute for the 2N4401 in certain circuits.
2N3055: A power NPN transistor commonly employed in power amplifier and voltage regulator circuits. It is not a direct substitute for the 2N4401 in low-power applications.
2N3906: A PNP transistor complement to the 2N3904, used for similar general-purpose applications but with opposite polarity.
2SC5200: A high-power NPN transistor often used in audio amplifier circuits. It is not a direct substitute for the 2N4401 but serves different applications.
2N551: An NPN transistor suitable for general-purpose applications. It may be used in circuits where characteristics similar to the 2N4401 are required.
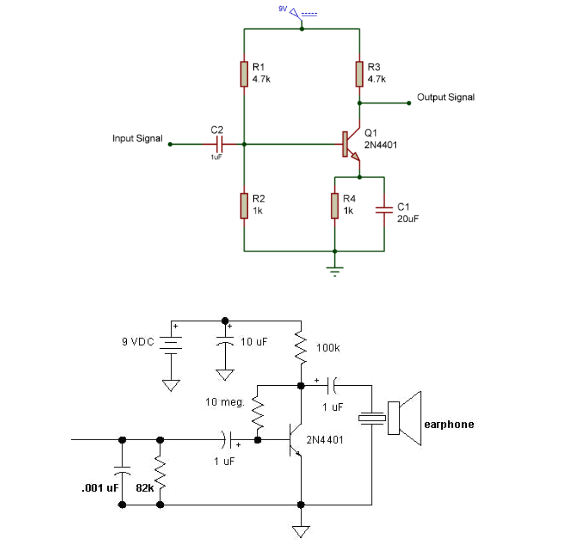
This is a basic circuit to configure a transistor as a switch. Please be aware that practical circuit adjustments might be necessary. I've employed a 5V base voltage and a 1K current-limiting resistor.
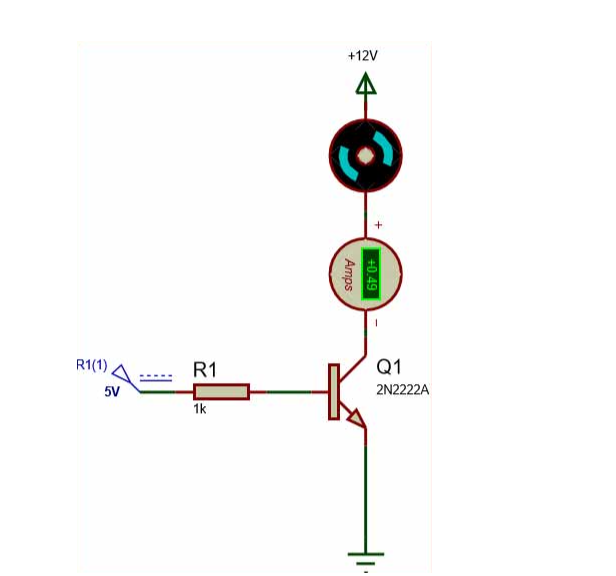
Keep in mind that the motor in this setup draws approximately 500mA from a 12V power source. Given the 2N4401's collector current rating of up to 500mA, this configuration is feasible. However, if a BC547 were used, the transistor would risk overheating and damage.
In the 2N4401 transistor, the beta (β) value plays a crucial role in characterizing the amplification capability of the device. Beta is defined as the ratio of the collector current (IC) to the base current (IB), representing the gain of forward current through the transistor. The beta value, denoted by 'β,' is essentially an amplification factor.
In the case of the 2N4401, the beta value can vary within a broad range, typically spanning from 20 to 1000. This range reflects the transistor's ability to amplify signals effectively. While the potential beta values cover a wide spectrum, the typical or nominal value for beta in the 2N4401 is specified as 200.
This amplification factor is a critical parameter when designing circuits using the 2N4401, as it influences the relationship between the input base current and the resulting output collector current.
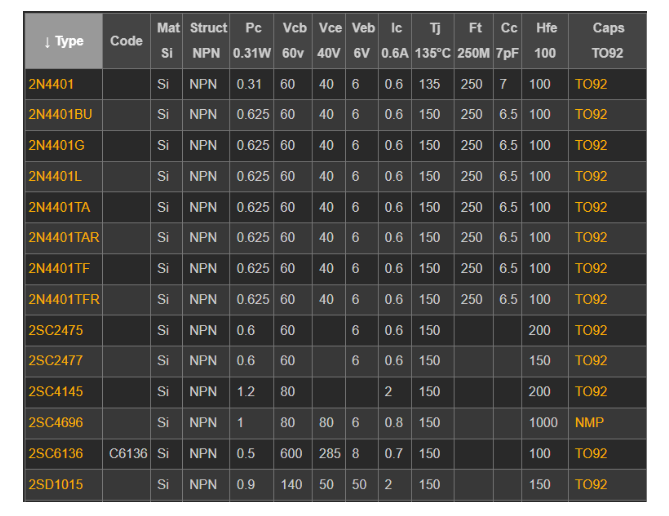
The 2N4401 has a higher collector current limit of 500mA compared to the 2N2222. This higher collector current rating allows the 2N4401 to handle medium loads more effectively. Additionally, the 2N4401 has a power dissipation of 652mW, which indicates its ability to dissipate heat and handle power more efficiently than the 2N2222.
Due to its higher collector current limit and power dissipation, the 2N4401 is well-suited for applications involving medium loads. This makes it a preferred choice in scenarios where higher current requirements are necessary, providing a reliable solution for driving moderate-sized loads.
The 2N3904 appears to be better optimized for operation at lower currents compared to the 2N4401. This optimization may make the 2N3904 a preferred choice in applications where lower current levels are a primary consideration.
Despite their differences, for a significant number of applications, the variances between the 2N4401 and 2N3904 may not be substantial enough to significantly impact performance. Consequently, they are often considered effectively interchangeable in such scenarios. The choice between the 2N4401 and 2N3904 may depend on specific requirements of the application, such as current levels, power dissipation, and voltage ratings.
2N4401, with its 500mA collector current limit, can drive loads greater than the BC547. This suggests that the 2N4401 offers advantages in terms of current-handling capability compared to the BC547 transistor, providing a viable alternative in applications with higher current demands.
The 2N4400 and 2N4401 transistors constitute a complementary pair, with the 2N4400 being a PNP type and the 2N4401 an NPN type. Both transistors, made of silicon, share similarities in power dissipation, voltage ratings, current gain, junction temperature, and package type. The key distinction lies in their polarity, influencing their interchangeability in electronic circuits. Typically used together in complementary configurations, these transistors offer versatile solutions for applications requiring NPN and PNP transistors with similar performance characteristics.
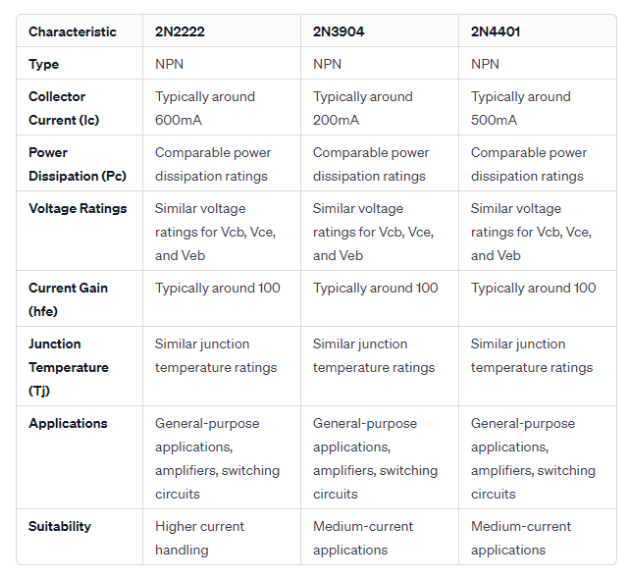
The 2N4403 is the PNP complementary transistor to the 2N4401. Both transistors, 2N4401 (NPN) and 2N4403 (PNP), are part of a complementary pair, which means they have opposite polarities and can be used together in various electronic circuits for complementary switching or amplification.
2N4403 Specifications:
Type: PNP
Material: Silicon (Si)
Structure: NPN
Pc (Power Dissipation): Typically around 0.6W
Vcb (Collector-Base Voltage): 40V
Vce (Collector-Emitter Voltage): 40V
Veb (Emitter-Base Voltage): 6V
Ic (Collector Current): 0.6A
Tj (Junction Temperature): 150°C
Ft (Transition Frequency): Typically 100MHz
Cc (Collector Capacitance): Typically around 7pF
Hfe (DC Current Gain): Typically 100
Caps: TO-92 Package
The 2N4403, being a PNP transistor, complements the characteristics of the 2N4401, allowing for versatile applications in electronic circuits where NPN-PNP pairs are required for proper operation.
The 2N4401 transistor is a versatile component widely employed in electronic circuits for diverse applications. Its utility extends to sensor circuits, audio preamplifiers, and amplifier stages, showcasing its proficiency in signal amplification. Additionally, the transistor excels in switching loads under 500mA, contributing to motor speed control and finding application in Darlington pairs for enhanced current gain. With capabilities suitable for radio frequency circuits under 250MHz and compatibility with inverter and rectifier circuits, the 2N4401 proves to be a fundamental building block in various electronic systems, offering flexibility and reliability across a spectrum of applications.
The 2N4401 transistor emerges as a cornerstone in electronic design, offering a potent blend of versatility and performance. Its specifications, pinout, and applications showcase the breadth of its capabilities, empowering engineers and enthusiasts to leverage its strengths in a myriad of electronic circuits. Whether amplifying signals, controlling motors, or participating in intricate switching scenarios, the 2N4401 remains an indispensable component in the world of electronics.